Outreach Efforts Getting More Vaccinated
Health clinics, literacy centers reaching out to immigrants and low-income people.

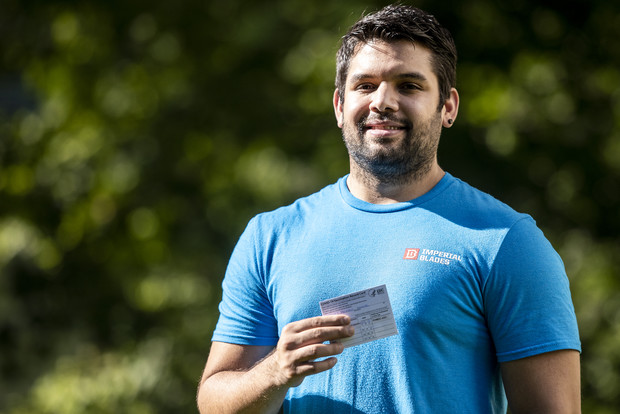
Miguel Marquez holds his COVID-19 vaccination record card Wednesday, June 30, 2021, near his home in Fitchburg, Wis. Angela Major/WPR
More people in immigrant and minority communities are getting vaccinated against COVID-19 in Wisconsin. That’s in part the result of focused outreach efforts, involving places you might not expect, such as literacy classes for immigrants, and also more likely locations, like free health clinics.
The efforts are geared toward those who want the vaccine or are on the fence.
“We’re talking about the unvaccinated but willing,” Agoada said. “We’re not looking at anti-vaxxers or folks that talk about conspiracy theories and will never have their position changed. We are looking at individuals who, because of logistical reasons, or they haven’t been approached in the right manner, have not yet gotten access to the vaccine.”
One of them is HealthNet of Rock County in Janesville where Yolanda Orosco-Arellano got vaccinated against COVID-19. Many of the clinic’s case managers and outreach workers speak Spanish, and one speaks Arabic.
Her case manager and one of the clinic’s interpreters, Alicia Alvarado, related how Orosco-Arellano wanted to get the vaccine even though she has other family and friends who are “too scared” to get a shot. Some wrongly believe a myth that getting vaccinated involves implanting a microchip, a persistent falsehood that health officials encounter.
Orosco-Arellano got the vaccine as soon as she was able, concerned her diagnosis of anemia might make her more susceptible to a bad case of COVID-19 if she were infected. Research has shown iron deficiency can weaken the immune system.
Alvarado drove Orosco-Arellano to her first dose in May.
Her three children, age 24, 21 and 12, are also protected against COVID-19, a process that began for the family in May and ended in mid-August.
The clinic’s flexible hours allowed Orosco-Arellano to get both shots without missing work as a hotel housekeeper in Janesville, where she lives after moving to Wisconsin from Oaxaca, Mexico.
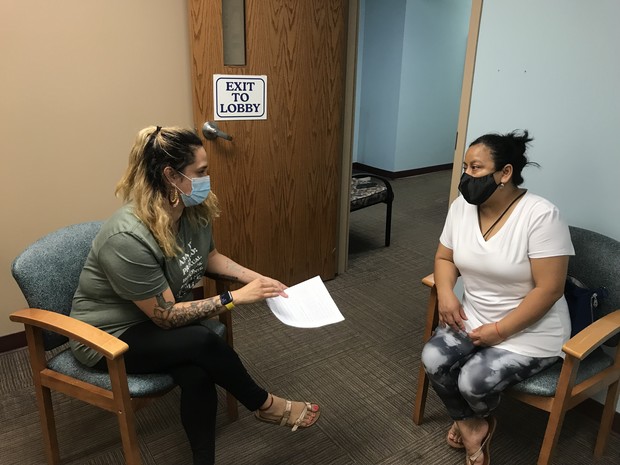
Staff at Janesville’s free clinic, HealthNet, discuss COVID-19 vaccines with clients. In this Aug. 2021 photo, translator and case manager Alicia Alvarez, left, provides information to Yolanda Orosco-Arellano, right, who decided to get vaccinated against the disease along with her three children. Shamane Mills/WPR
For other workers, though, that can be a big barrier, says HealthNet of Rock County CEO Ian Hedges.
“Folks who come to our clinic are working labor-intensive jobs on a shift schedule. Farming. Factory work. They have a hard time missing work not only to get the shot but what happens if they get sick afterwards,” as immunity starts to kick in, Hedges said.
HealthNet of Rock County has worked with large employers like MacFarlane Pheasants in Janesville. The company made sure workers had time off and transportation to vaccination sites.
“They were incredibly proactive,” Hedges said of MacFarlane Pheasants, the largest pheasant producer in North America, according to its website.
But time and transportation are just two factors. Equally important is trust.
“It’s not about ‘We will provide access, and they will come,'” explained Hedges. “It’s about making a true investment and having those conversations. That sounds silly, but for years health care institutions and city governments may not have been making those relationships. So when they opened up to the vaccines and wondered, ‘Why are folks not coming?’ Well, it’s because those relationships weren’t there. That trust wasn’t there.”
Statewide, nearly 42 percent of the Hispanic community is vaccinated. That’s lower than the state overall but higher than the share of Black residents who are vaccinated.
HealthNet of Rock County is one of a dozen free clinics in Wisconsin that is part of a national effort called Project Finish Line that aims to get 1 million shots into the arms of the country’s hardest-to-reach individuals by the end of the year. It’s overseen by Sostento, a New Jersey nonprofit that says it works to “alleviate public health workers’ toughest challenges so they can save more lives.”
Young, Healthy, And Now Vaccinated
Eight months after COVID-19 vaccines first became available, the protections provided against the disease remain uneven, but some racial and ethnic gaps are narrowing in Wisconsin.
While the rate of white residents getting vaccinated has dropped off, the rate of Asian, Hispanic, Native and Black residents getting vaccinated has remained higher than white residents since June, according to state data.
In absolute numbers, the share of shots given overall reflects the state’s demographics, with white residents rolling up their sleeves the most. But Asian communities now have the largest share of vaccinated people at 54 percent, the data shows.
A woman who was born in South Korea and moved to Madison learned about the vaccine in a rather unusual way: during a literacy class. In addition to teaching students English, the instructor also answered questions about the COVID-19 vaccine.
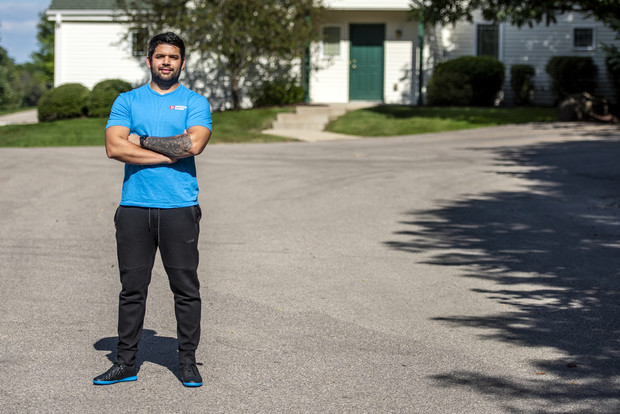
Another classmate explained how a co-worker did not want the vaccine but later changed her mind as more people were vaccinated. As for himself, 29-year-old Miguel Marquez initially thought he didn’t need the vaccine because he was young and healthy. But then the Venezuela native changed his mind after seeing younger people hospitalized, with some even dying.
“At that moment I knew it’s bad. It’s actually happening. So I was worried,” said Marquez, who came to Madison in 2019.
He doesn’t understand why some people in the United States are resisting getting vaccinated when people in his homeland and other countries are begging for COVID-19 shots that are hard, if not impossible, to get.
“You can get the vaccine but in other countries they can’t. And if they can, they to pay money they don’t have,” he said.

Miguel Marquez holds his COVID-19 vaccination record card Wednesday, June 30, 2021, near his home in Fitchburg, Wis. Angela Major/WPR
How Successful Are Vaccine Outreach Efforts?
In April, the Madison-based Literacy Network surveyed its adult learners to find out how many were vaccinated against COVID-19 and found out less than a third were, 11 percent lower than Dane County as a whole at the time.
Time and discussions that quelled concerns helped boost the rate of vaccinated adult learners in the program to 78 percent by mid-June, said Literacy Network instructor Marie Simpson.
The Literacy Network not only developed vaccine lesson plans, the group created social media posts with accessible, accurate vaccine information. It also hosted two vaccine clinics in partnership with the Fitchburg Community Pharmacy.
The Literacy Network received $13,000 from the Wisconsin Department of Health Services for its vaccine outreach program.
Meanwhile, in Janesville, the free clinic HealthNet of Rock County administered more than 3,200 COVID-19 shots from February to the end of July. That’s more than some federally qualified health clinics and higher than some rural hospitals in the area, Hedges said.
Listen to the WPR report here.
Time, Extra Effort And Trust: Local Organizations Increase COVID-19 Vaccine Uptake In Hard-To-Reach Communities was originally published by Wisconsin Public Radio.
More about the Coronavirus Pandemic
- Governors Tony Evers, JB Pritzker, Tim Walz, and Gretchen Whitmer Issue a Joint Statement Concerning Reports that Donald Trump Gave Russian Dictator Putin American COVID-19 Supplies - Gov. Tony Evers - Oct 11th, 2024
- MHD Release: Milwaukee Health Department Launches COVID-19 Wastewater Testing Dashboard - City of Milwaukee Health Department - Jan 23rd, 2024
- Milwaukee County Announces New Policies Related to COVID-19 Pandemic - David Crowley - May 9th, 2023
- DHS Details End of Emergency COVID-19 Response - Wisconsin Department of Health Services - Apr 26th, 2023
- Milwaukee Health Department Announces Upcoming Changes to COVID-19 Services - City of Milwaukee Health Department - Mar 17th, 2023
- Fitzgerald Applauds Passage of COVID-19 Origin Act - U.S. Rep. Scott Fitzgerald - Mar 10th, 2023
- DHS Expands Free COVID-19 Testing Program - Wisconsin Department of Health Services - Feb 10th, 2023
- MKE County: COVID-19 Hospitalizations Rising - Graham Kilmer - Jan 16th, 2023
- Not Enough Getting Bivalent Booster Shots, State Health Officials Warn - Gaby Vinick - Dec 26th, 2022
- Nearly All Wisconsinites Age 6 Months and Older Now Eligible for Updated COVID-19 Vaccine - Wisconsin Department of Health Services - Dec 15th, 2022
Read more about Coronavirus Pandemic here






















