New Marquette Law School Poll national survey finds majority of public opposed to overturning Roe v. Wade, yet closely divided on 15-week abortion limit
MILWAUKEE —Forty-nine years after the U.S. Supreme Court ruled in favor of a constitutional right to abortion, the public opposes overturning the 1973 Roe v. Wade ruling but is closely divided on limiting abortions after 15 weeks of pregnancy.
A new Marquette Law School Poll national Supreme Court survey finds that, among those with an opinion on Roe, 28% say they are in favor of overturning the decision and 72% are opposed to overturning it. The case before the Court that includes argument for overturning Roe, Dobbs v Jackson Women’s Health Organization, concerns a Mississippi law that restricts abortion after 15 weeks of pregnancy. Asked about that specific restriction, among those with an opinion, 49% favor that limitation on abortion, while 51% oppose it.
There has been little shift in opinion on overturning Roe since September, as shown in Table 1. Opinion on Dobbs, shown in Table 2, has remained closely divided, but has shifted slightly to being more opposed to the restrictions at issue in Dobbs since September. The percentages in the tables show results among those with an opinion of each case.
Table 1: Favor or oppose overturning Roe v. Wade, among those with an opinion, Jan. 2022
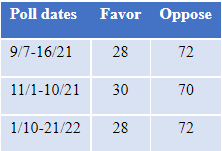
Table 1: Favor or oppose overturning Roe v. Wade, among those with an opinion, Jan. 2022
Table 2: Favor or oppose upholding 15-week abortion ban in Dobbs, among those with an opinion, Jan. 2022

Table 2: Favor or oppose upholding 15-week abortion ban in Dobbs, among those with an opinion, Jan. 2022
As the abortion issues before the Court have received more attention since summer, the percentage of respondents with an opinion about Roe has increased. In September, 71% said they had an opinion on reversing Roe; the number rose to 77% in January. There was little change in the number holding an opinion on Dobbs, which was 73% in September and 74% in January.
A Texas law, Senate Bill 8 (SB-8), is favored by 28% and opposed by 72% of those with an opinion about the law. SB-8 bans abortions after about six weeks of pregnancy, once fetal cardiac activity can be detected, and authorizes individual citizens to sue those who aid others in getting an abortion. In this survey, 81% say they have an opinion about this law. In November, 30% of those with an opinion favored the law, while 70% opposed it. In November, 84% had an opinion on this issue.
Views of the abortion issue differ by partisanship, with Republicans the only partisan group in which a majority favors overruling Roe v. Wade, as shown in Table 3.
Table 3: Percent who favor or oppose overturning Roe, among those with an opinion, by party identification, Jan. 2022
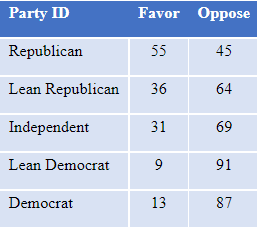
Table 3: Percent who favor or oppose overturning Roe, among those with an opinion, by party identification, Jan. 2022
Support for upholding the 15-week ban in Dobbs draws more support across all party groups, though with a sharp gradient from Republicans to Democrats, shown in Table 4.
Table 4: Percent who favor or oppose upholding 15-week abortion ban at issue in Dobbs, by party identification, Jan. 2022, among those with an opinion
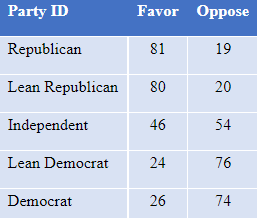
Table 4: Percent who favor or oppose upholding 15-week abortion ban at issue in Dobbs, by party identification, Jan. 2022, among those with an opinion
Partisan support for the Texas SB-8 law falls between that for overturning Roe and that for upholding the restriction at issue in Dobbs, among those with an opinion of the law, as shown in Table 5.
Table 5: Percent who favor or oppose Texas SB-8 law, among those with an opinion, by party identification, Jan. 2022
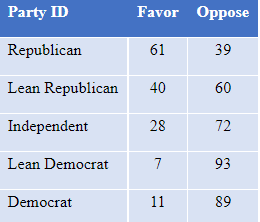
Table 5: Percent who favor or oppose Texas SB-8 law, among those with an opinion, by party identification, Jan. 2022
Gun rights
This survey asked if the respondent would favor or oppose a decision “that the Second Amendment right to ‘keep and bear arms’ protects the right to carry a gun outside the home.” Among those with an opinion, 67% say they favor such a ruling, while 33% are opposed. In September, 63% of those with an opinion favored such a ruling and 37% were opposed. In this January survey, 75% had an opinion on this issue, whereas 70% had an opinion in September.
Views on the right to possess a gun vary with partisanship, with overwhelming support among Republicans and only minority support among Democrats, as shown in Table 6.
Table 6: Percent who favor or oppose right to carry a gun, by party identification, among those with an opinion, Jan. 2022
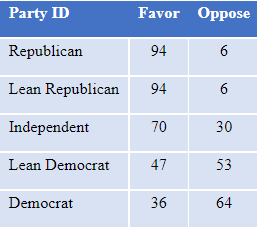
Table 6: Percent who favor or oppose right to carry a gun, by party identification, among those with an opinion, Jan. 2022
Those with a gun in the household are much more supportive of a right to carry a gun outside the home, as shown in Table 7. Those without a gun in the household are about evenly split, while a large majority of gun householders support a right to carry. Gun owners are also more likely to have an opinion on the issue, 79%, than are those without guns in their home, 72%.
Table 7: Percent who favor or oppose right to carry a gun, by whether there is a gun in the household, among those with an opinion, Jan. 2022
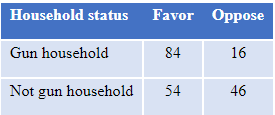
Table 7: Percent who favor or oppose right to carry a gun, by whether there is a gun in the household, among those with an opinion, Jan. 2022
Views of vaccine mandates
On Jan. 13, the Court stopped the federal Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) from enforcing a rule that would have mandated companies of more than 100 employees to require employees to either be vaccinated or be regularly tested for COVID19. The Court held the rule to be likely unlawful and stayed its enforcement pending further consideration of challenges to the mandate in the U.S. Court of Appeals for the 6th Circuit. At the same time, the Court ruled that the federal government could require vaccination of health care workers at facilities that receive Medicare or Medicaid funding.
Asked about these policies, 54% favor the OSHA requirement, with 45% opposed, while 61% favor requiring vaccinations for health care workers and 38% are opposed.
Approval of the Supreme Court
Approval of the U.S. Supreme Court remains evenly divided, with 52% approving and 46% disapproving. Approval declined from 60% in July to 49% in September and has changed little since then. The trend in approval of the Court since 2020 is shown in Table 8.
Table 8: Approval of the Supreme Court, Sept. 2020-Jan. 2022
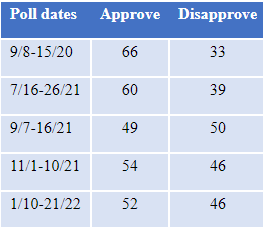
Table 8: Approval of the Supreme Court, Sept. 2020-Jan. 2022
Approval has fluctuated among Democrats after falling sharply in September, while there was little recent change among independents and Republicans. All partisan groups have lower approval now than in September 2020. Table 9 shows approval by party over five Marquette Law School Poll surveys since September 2020.
Table 9: Approval of the Supreme Court by party, Sept. 2020-Jan. 2022
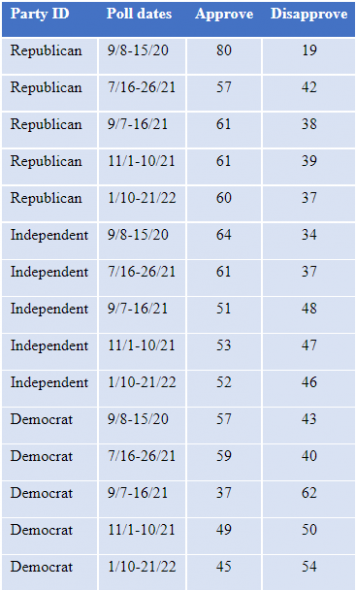
Table 9: Approval of the Supreme Court by party, Sept. 2020-Jan. 2022
Perceptions of the basis of decisions
- When asked about the justices’ motivation, 42% of this beginning-of-survey group say the justices are mainly motivated by politics and 58% say mostly by the law.
- In contrast, when asked about the Court, 53% of this beginning-of-survey group say the Supreme Court is mainly motivated by politics and 47% say it is mainly motivated by the law.
Then, the other half (again, randomly selected) of the survey respondents were asked one (or the other) of these two questions much later in the survey, after questions about favorability of the justices, ideological placement of the Court, and items about specific cases concerning abortion and gun rights among others. When asked later in the survey, the perception of the motivations for decisions as being politics increases for the wording of both questions—the one speaking of the “justices” and the one focused on the “Court” as a single body.
- When asked late in the survey, 55% say the justices are mainly motivated by politics and 45% say mostly by the law.
- When asked late in the survey about the motivation of the Court as a whole, 60% say the Court is mainly motivated by politics and 40% say mostly by the law.
The implication of this finding is that views of the Court as a single institution provoke the perception of a more political body—and that perception is increased after respondents are required by many questions to think about the Court. In contrast, when the focus is on the justices, respondents are more likely to believe “the law” is the motivation of the justices, although this percentage declines (to a minority) after a numerous questions have required the respondent to think more about justices and cases before the Court, whereupon there is approximately an even split in impressions of motivations for decisions.
This reflects some difference in how citizens think about the motivations of individual justices and how they think of the Court as a whole. It also demonstrates that when people are prompted to think about the controversial cases before the Court, the percentage who see political motivations for both the justices and the institution increases.
Table 10 summarizes the results concerning the basis of decision.
Table 10: Basis of decision, by question focus and placement in survey, Jan. 2022
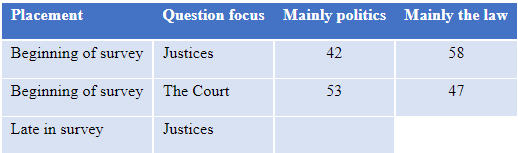
Table 10: Basis of decision, by question focus and placement in survey, Jan. 2022
NOTE: This press release was submitted to Urban Milwaukee and was not written by an Urban Milwaukee writer. While it is believed to be reliable, Urban Milwaukee does not guarantee its accuracy or completeness.
Mentioned in This Press Release
Recent Press Releases by Marquette University
Lucas Lawas Earns Spot on BIG EAST Honor Roll
Apr 7th, 2025 by Marquette UniversityLawas notched a career-best 17 saves against then-No. 14 Georgetown on Saturday
Marquette Law Poll supplement: Open-ended answers offer insights on Trump favorability
Dec 18th, 2024 by Marquette UniversityTrump earned 53% approval in national survey released Dec. 18






















